Mobile applications are the first media we use to access information from our smartphones and tablets. We easily trust them with sensitive data, but what do we know about their security levels? Organizations develop mobile applications at a fast pace to keep up with business needs and often leave aside security measures.
In a recent survey aiming at diagnosing companies GDPR compliance, Pradeo asked 382 security leaders about the way they develop mobile applications, the data they manipulate and the security process they go through.
Check the statistics we published last week about security related to organizations’ mobile devices.
Here are the main highlights of this research:
- 83% of organizations externalize the development of their mobile applications
- 67% of mobile applications manipulate user’s data
- 25% of respondents do not secure their mobile applications
Mobile application development is mostly externalized
Among the organizations that develop mobile applications, 83% fully externalize their developments and 79% embed third-party libraries within their apps. When they don't undergo security testing, third-party developments often cause unexpected behaviors and data leakage without their distributors knowledge.
4 in 5 organizations
externalize their apps development
Most mobile applications manipulate confidential data
Data privacy regulations (GDPR, PIPEDA…) are enforced around the world to protect personal data. When a mobile application manipulates users’ contact list, pictures, email, etc., it must comply with those regulations by ensuring data protection and transparent process.
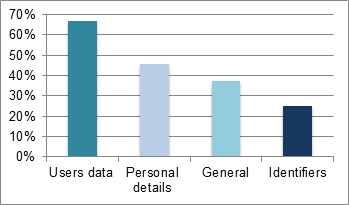
Respondents stated that the applications they develop manipulate:
- Users data (SMS, call logs, contacts, pictures, audio, calendar): 67%
- Personal details (email, name): 46%
- General data (service provider, country code, OS provider...): 38%
- Identifiers (IMEI, credentials...) 25%
Many applications are still not secured
While most of their mobile applications handle sensitive data, some organizations still do not secure them.
- Internal threat protection: 25% of companies do not test their applications for unexpected behaviors and vulnerabilities. As a result, their apps could secretly perform unnecessary and malicious actions or embed flaws that could weaken their resistance to attacks.
- External threat protection: 25% of companies do not embed any application self-protection security module within their applications. Consequently, they are highly exposed to threats coming from the mobile environment they are running on.
Furthermore, only 58% of organizations which applications manipulate personal data stated they record data processing activities related to their mobile apps. However, it constitutes a direct infraction to the GDPR Article 30 which requires organizations to “maintain a record of processing activities under their responsibility”.
Download Our Mobile Application Security Guide



.png)
-2.png)
-3.png)

