Introduced for the first time in 2001 under the UNIX system, the ARP protocol (Address Resolution Protocol) enables to establish a communication by associating on a local network the IP address and the MAC address (Media Access Control) of a device. The attack that exploits this protocol, called ARP spoofing or ARP poisoning, enables a hacker to divert the information exchanged on the network to his own computer, mobile, server... Historically targeting computers, this type of attack is just as efficient on mobile devices and IoT.
What is the ARP protocol?
In order to build Ethernet frames during a network exchange, the ARP protocol associates the MAC address of a device with an IP address. For the frame to be complete and the data to be able to transit, the MAC and IP address must be linked. The role of ARP is therefore a prerequisite for a secure exchange on the network.
Ordinary routing
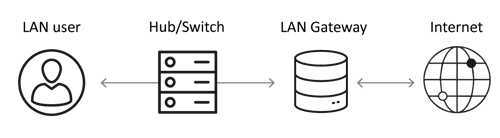
Routing under ARP attack
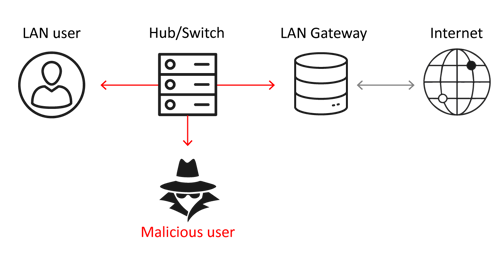
More specifically, the protocol works in three steps:
- New incoming request: A device wants to send a network packet to a recipient whose IP address is known.
- Resolution: Since communication by IP address only is impossible, the ARP table associates the received IP address with a MAC address.
- Sending the request: If the ARP table does not know a MAC address to associate, the sender sends an ARP request to query the network and get the missing MAC address.
ARP Spoofing : mechanism and results
Traffic hijack
The goal of ARP poisoning is to hijack packets that are exchanged between a legitimate user and a server. Does this sound like a Man-in-the-Middle attack? Well that's normal, because ARP poisoning or spoofing is a step of a Man-in-the-Middle attack!
In case of rerouting to steal information, the hacker spies on the packets that are exchanged but forwards them to the legitimate server. Thus, the user does not notice any difference and the spying follows its course.
- The user initiates a communication which is established normally in appearance, because of an ARP table falsified by the hacker.
- The hacker intercepts the information passing through the network and forwards it to the server.
- The server is answering correctly to the initial request, everything seems normal.
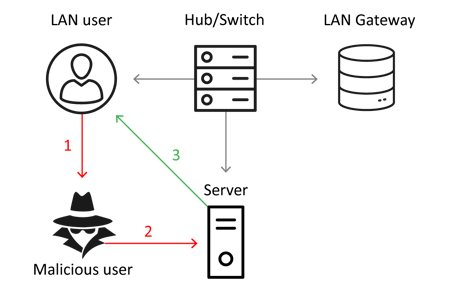
Denial of service (DoS)
In another context, a hacker can completely or partially interrupt a company's network traffic in order to paralyze its information system and its business. To do this, the steps are identical to the first case explained above, but the intercepted communication is not forwarded to the server. The information then goes directly to the hacker and is blocked there. Not very discreet, this attack causes a denial of service. It can be used in addition to a ransom demand to restore the network.
How to protect your device from ARP poisoning?
Pradeo Security Mobile Threat Defense protects mobile fleets against ARP spoofing/ARP poisoning by monitoring the integrity of devices' connections in real time.
To know more, visit our Mobile Threat Defense page.

.png)
.png)


