Workers are undeniably mobile with 80% of corporate tasks to take place on mobile devices in 20201. With 77% of the digital traffic2 coming from smartphones and tablets, mobile protection comes as a central piece of the information security strategy of companies.
The advent of mobility drew a new paradigm where security gates have to be relocated beyond the enterprise perimeter. In that framework, legacy security practices are falling short to address a landscape characterized by a plethora and dynamicity of threats.
Armed with the conclusion, CISOs and security heads move in search of the suitable mobile security solution to match their corporate security needs and dive into the mobile security ecosystem. If this is the right step forward, they usually end up more confused rather than enlightened, flooded by the diversity of players more or less pretending to have similar capabilities.
This article aims at clarifying the area of expertise of each kind of solution, the security capabilities they are delivering to mobile devices as well as mistruths, erroneous statements and as a consequence pitfalls to avoid.
Mobile security core principles
Prior deep diving into the capabilities delivered by each family of players, it is key to set the scene of the foundations of mobile security so as to have a solid comparison grid to move forward.
The two pillars of security are both threat identification and remediation
Although it seems quite self-evident when stated, it is key to look at the mobile security ecosystem in the light of those two requirements. When assessing a solution, we shall closely examine all the security measures offered to thwart attacks and might overlook detection capabilities. This approach is rooted to desktop methods where the static enforcement of security used to stand at the heart of the protective posture.
This logic fades in the face of a constantly evolving threat landscape directly targeting mobile devices. Setting up boundaries without a clear visibility on threats would be unproductive and generate a lot of frustration for mobile users. Therefore, detection abilities play a decisive role in the protection of mobile workers and as to be equally balanced with response aspects.
Mobile security is a specific cybersecurity area
A common pitfall when considering protecting the mobile workforce is to basically extend the existing concepts to mobile devices. But security principles successful to laptops and PCs, which primarily rely on a structuring piece being the firewall to ward off most of the attacks, are definitively not adapted to the vivacity of mobile threats. Therefore, legacy practices are to be considered outdated when addressing mobile security.
Mobility reinvented and mixed personal and professional usages and opened in parallel a fruitful breach for hackers. Data is now accessed but also hosted on mobile devices which become as many targets. The dark web is chock-full of data brokers monetizing 1 million active users’ data for $4000 USD/month3.
Mobile cyber threat intelligence is a dedicated domain of expertise to provide adapted detection capabilities and counter measures for the mobile environment. The democratization of apps and the hyper-connectivity underlying mobile usages drive an entirely new approach of security.
An effective security solution for mobile must provide innovative and advanced functionalities to keep up with mobile cyber-criminality and pretend to an effective security.
Mobile security solutions
The following representation shows the perimeter of each solution constituting the mobile security ecosystem and the way those solutions complement each other.
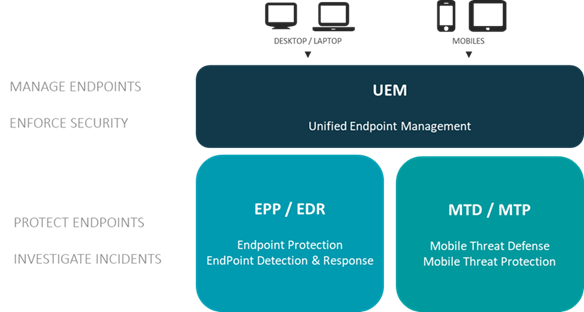
UEM security – EMM security – MDM security
Primarily known as Mobile Device Management (MDM), this field reshaped its market positioning over the last years and changed its name accordingly: firstly changing for Enterprise Mobile Management (EMM) and lastly for Unified Endpoint Management (UEM).
Still it covers the overall same functional surface and arises from the need to manage endpoints by providing core administration features (device identification, distribution of corporate resources, …).
Taking a closer look to threat protection, UEM security capabilities are dedicated to the enforcement of company security safeguards. The administrator manually set its security context and implement additional measures in case of reporting of a threat (containerization, conditional access to resources).
The detection of threats is not scoped as part of UEM functionalities and is to be provided by a complementary solution. Mobile threat defense solutions are usually integrated with the major UEM players to provide on-device threat detection and remediation and trigger additional security safeguards within the UEM solution.
Pradeo Security solution is integrated with major UEM players such as Microsoft Inune, VMware Workspace ONE (Airwatch), MobileIron and others.
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) - Endpoint Protection (EPP)
Endpoint Detection and Response and Endpoint Protection is a wide area reflecting the revamping of antivirus solutions. It addresses desktop and server viral threats and is timidly extending to mobiles. EDR and EPP solutions are focused on malwares and low layers attacks. They are automatically blocking known threats and reporting activities to a central console for investigation. The remediation comes from an automatic action or a human decision from the Security Operating Center (SOC).
As far as mobile is concerned, EDR and EPP players are providing antivirus capabilities and open their system to aggregate mobile threat intelligence coming from solutions dedicated to mobile protection. For instance, Pradeo Security Mobile Threat Defense feeds VMware Workspace ONE Intelligence and Microsoft Defender ATP with mobile security insight.
Mobile Threat Defense (MTD) - Mobile Threat Protection (MTP)
Mobile Threat Defense and Mobile Threat Protection solutions are EDR shaped for the spectrum of mobile cyber-threats. Those solution emerged from the advent of mobility and the shifting of cyber-criminality towards the newly mobile data centric usages.
Mobile Threat Defense solutions are now commonly covering app, network and device threats but players did not build their expertise the same way.
Some players, such as Pradeo, primarily focused on App threats detection and usually offer an application security testing service such as Pradeo. Applications revolutionize mobile usages with fast developed and widely accessible services overwhelming signature-based threat detection techniques. Application analysis requires a cutting-edge threat intelligence approach to provide a dynamic and accurate assessment.
The other players concentrated on network and OS layers, adapting desktop threat detection techniques to the mobile environment.
Ultimately, both kind of players integrated the missing part into their solution to deliver a 360° protection. However, application analysis being a structuring piece to be added, detection and as a result response capabilities are not evenly balanced between players.
With application representing 76% of mobile threats, a specific attention is recommended when assessing a Mobile Threat Defense solution to ensure that application threat detection is not leading to numerous false-positives. The growing privacy concerns and data protection regulations require to implement a powerful solution drawing clear conclusion to avoid any end-user’s frustration, lake of visibility for security heads and default in the compliance with regulations.
As a conclusion, we could draw the following comparison grid as to assess the mobile security expertise and capabilities of solutions of the mobile security ecosystem.
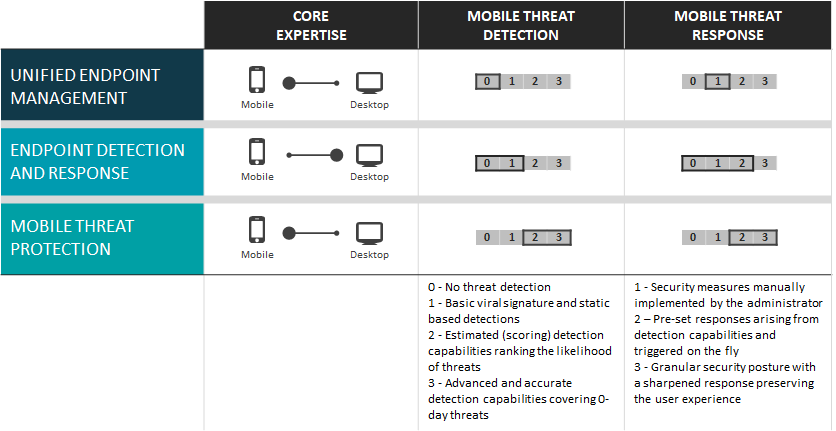
Sources:
1 - Gartner, Prepare for Unified Endpoint management to Displace MDM and CMT
2 - ComScore, Global state of mobile
3 - BuzzFeed



-1.png)
-1.png)
.png)

